| Previous chapter | Next section | Next chapter | |
| ToC | Computers And Internet | MPEG-4 Inside – Advanced Video Coding | Software And Communication |
The MPEG File Format has been designed to satisfy a set of requirements, some of which are listed below
- Binary assets
- Hierarchical structure
- Backward- & forward-compatible
- Suitable to hold timed content
- Suitable to exchange content
- Self-contained (only contain data to be exchanged or all of them)
- Content can extend on more than one file
- Suitable for editing
- Suitable for streaming
- Can playback local file
- Can download and play the file
- Object oriented
- Separated content and metadata
The figure below depicts the MP File hierarchy in a specific instance
F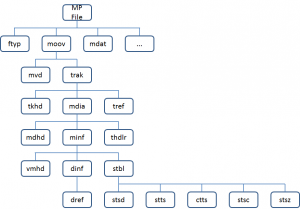 Figure 1 – an example of MP File hierarchy
Figure 1 – an example of MP File hierarchy
The meaning of some the boxes are
- ftyp (File Type): File type, version
- mdat (Media Data): Holds media data (several, non contiguous possible)
- moov (Movie): Holds metadata of a presentation
- mvhd (Movie Header): General info about the movie
- trak (Track): Holds metadata related to one stream
- hdlr (Handler): Stream type
- dinf/dref (Data Information/Data Reference): Data location (this or remote file)
- stbl (Sample Table): Holds metadata related to samples, sample by sample
- stsd (Sample Description): decoder configuration for the elementary stream
- stts (Sample To Time): DTS for each sample
- stsz (Sample To Size): Size of each sample
| Previous chapter | Next section | Next chapter | |
| ToC | Computers And Internet | MPEG-4 Inside – Advanced Video Coding | Software And Communication |