Six months after leaving my employer of 32 years, I became CEO of CEDEO, an Italian company I had already a participation in, and made it the vehicle of my forays into the new business of technology use. Today the mission of CEDEO is
To conceive, design, implement, deploy and operate advanced digital media solutions based on smart combinations of new technologies and standards for the next phase of pervasive media-enabled communication
I claim there is substance besides the nice words. CEDEO started from the consideration that many video platforms exists today on the Web, but none, if not for limited contexts, offers platform users – i.e. any player in the video content life cycle: content creators, providers, distributors etc. – the means to do business with other platform users. In other words, support to business is regularly “client- server”, not “peer-to-peer”.
Letting peer do business in a peer-to-peer fashion is exactly what WimTV does, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 – The basic WimTV services and applications
A user can
- Import his content to a private digital locker (WimBox)
- Post his content to WimTrade for other users to acquire rights to it or acquire rights to another user’s content
- In case he has not found what he was looking for, post to WimTrade a “request for content” that satisfies specific user requirements
- Respond to a request for content using WimTrade or, if on the move, WimLance (an app for Android and iOS)
- Post content of which he has rights (e.g. acquired from WimTrade) to his WebTV for users to watch (WimVod)
- Create an event and make it available for other people to watch live at the scheduled time and on demand after the event is over
- Create a schedule that streams a sequence of videos and/or live events as if it were a TV
- Watch WimTV content from his PC or SmartTV/mobile device using WimView
- Export content of which he has rights (e.g. acquired from WimTrade) from his WimBox
A user can populate his WimBox with assets in 3 different ways:
- By importing content of which he has rights to WimBox
- By acquiring rights to other users’ content from WimTrade
- By creating and posting a request for content (WimTrade) satisfying specific requirements.
A user can monetise his assets in WimBox in 3 different ways:
- Make public and private (i.e. restricted) offers in WimTrade
- Export content of which he has rights for a variety of delivery channels: Web, IPTV, 3G/4G, broadcast
- Post to WimVod and stream content of which he has rights to end users.
It should be no surprise that, say, YouTube and WimTV are worlds away. This can be seen from two excerpts of the YouTube and WimTV Terms of Service. The bottom line is that, in the case of YouTube you upload content and then YouTube has the right to do business on it, while in the case of WimTV you upload content and you keep the right to do business with it. You can do this more successfully on WimTV than on your own because the WimTV platform offers you a variety of services.
| YouTube | WimTV |
| …These Terms of Service apply to all users of the Service, including users who are also contributors of Content on the Service. YouTube hereby grants you permission to access and use the Service as set forth in these Terms of Service, provided that You agree not to distribute in any medium any part of the Service or the Content without YouTube’s prior written authorization… |
…When you Import and Post Content to the Platform, you remain the sole owner of the rights to that Content and Company does not claim ownership of the materials. It is your responsibility to find one or more than one User that can help you distribute that content for eventual consumption by granting them appropriate Licences or to assume yourself the Role(s) that enable you to achieve that goal… |
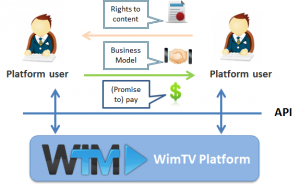
Fig. 2 depicts the essence of WimTVin a concise way: a platform where user A and user B can do business on the basis of the most fundamental of principles: they share a business model based on which user A gives right to his content to user B and user B pays a certain amount or promises to pay a certain amount or a share of his revenues every time a transaction based on the content takes place.
Figure 2 – Relationships between WimTV users
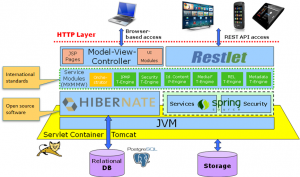
The WimTV platform provides a number of services that users can call when they do business on the platform. The platform is based on a low layer of very robust Open Source Software (OSS) layers and a middleware that makes reference to MXM.
Figure 3 – The WimTV architecture
The platform exposes a standard HTTP interface for browser-based access and a Representational State Transfer (REST) API that applications on a variety of devices can access.
These are some API
| User mgmt | Import/ export | On demand | Live | Trading | Payment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| – Register – Profile – List – Connections -…¦ |
– Upload – Progress Bar – Download – Delete – … |
– List Videos – Detail Video – Post – Remove -… |
– Create Event – List Events – Stream Event – EPG -…¦ |
– List – Post – Remove – Acquire -…¦ |
– VoD – Live – Subscription – Download -…¦ |
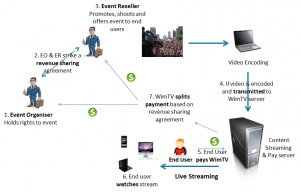
An example of the type of services provided by the WimTV platform is illustrated in Fig. 4. Here a user (called Event Organiser) sets up an event and makes an agreement with another user (called Event Reseller) to distribute the event, including the level of revenue sharing between them. The two users register on WimTV specifying their roles and informing WimTV of their revenue sharing arrangement. For every end user buying a “ticket” WimTV will split the revenues among itself and the two users and, between the two users according to the revenue sharing agreement.
Fig. 4 – WimTV live services
WimLive offers a number of features that are not found on othersystems
- Event Organiser and Event Reselles may coincide
- An arbitrary number of parties may claim rights to event
- Revenues are accredited as soon as a payment is effected
- WimTV acts as a trusted third party
- The service has low administrative costs (the burden is taken over by WimTV).
The platform offers WimTVPro, a WordPress, Joomla and Drupal plugin that replicates most WimTV functionalities on the user’sContent Management System (CMS). The user can then turn a website into an full-fledged video content management, distribution and commerce. Specifically
- To manage and publish videos on web pages or streaming dedicated widgets
- To publish on demand videos and video playlists, and stream live events with a single plugin
- To monetise videos published with professional pay-per-view licenses
WimTV is based on a simple but effective business model:
- Free use of WimTV services, apps, API to develop new services and apps
- Monthly subscription for the use of WimTV storage and streaming resources required by WimTV services/apps (existing/customer-developed)
- Revenue sharing with WimTV when services/apps generate revenues to user
- Platform licensing to users who intend to develop apps and offer services with licensee’s brand.